Introduction to SLAM (Cyrill Stachniss)
2021. 12. 20.Cyrill Stachniss 교수님의 강의를 정리한 것입니다. Youtube
What is SLAM?
로봇의 위치와 환경의 맵을 동시에 계산 하는것
- Localization : 로봇의 위치를 추정
- Mapping : 지도를 제작
- SLAM : Localization과 Mapping을 동시에 하는 것
정확한 Mapping 데이터가 있다면 Localization이 쉬움
정확한 Localization 데이터가 있다면 Mapping이 쉬움
→ 둘 다 해야되기 때문에 SLAM이 어렵다.
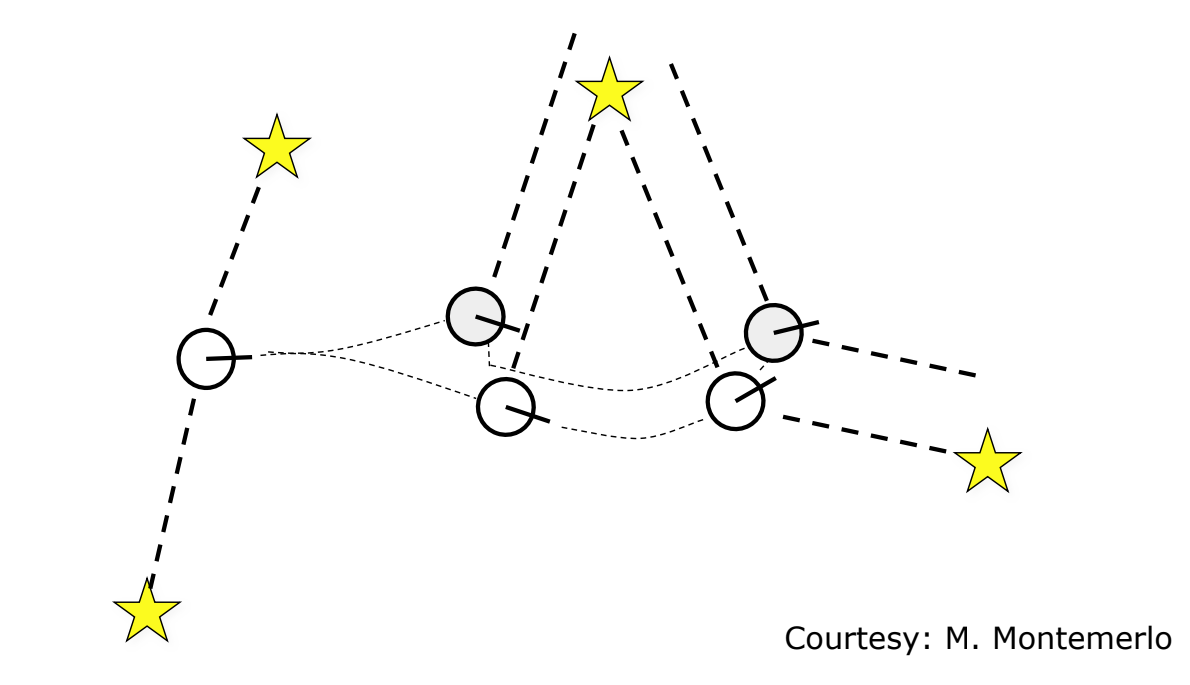
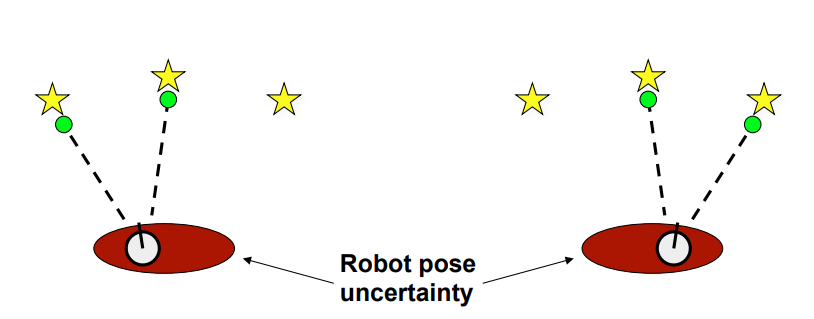
Localization Example
로봇의 위치를 주어진 Landmark로 보정
별 : Landmark
흰색 동그라미 : 실제 로봇의 위치
회색 동그라미 : 인지된 로봇의 위치
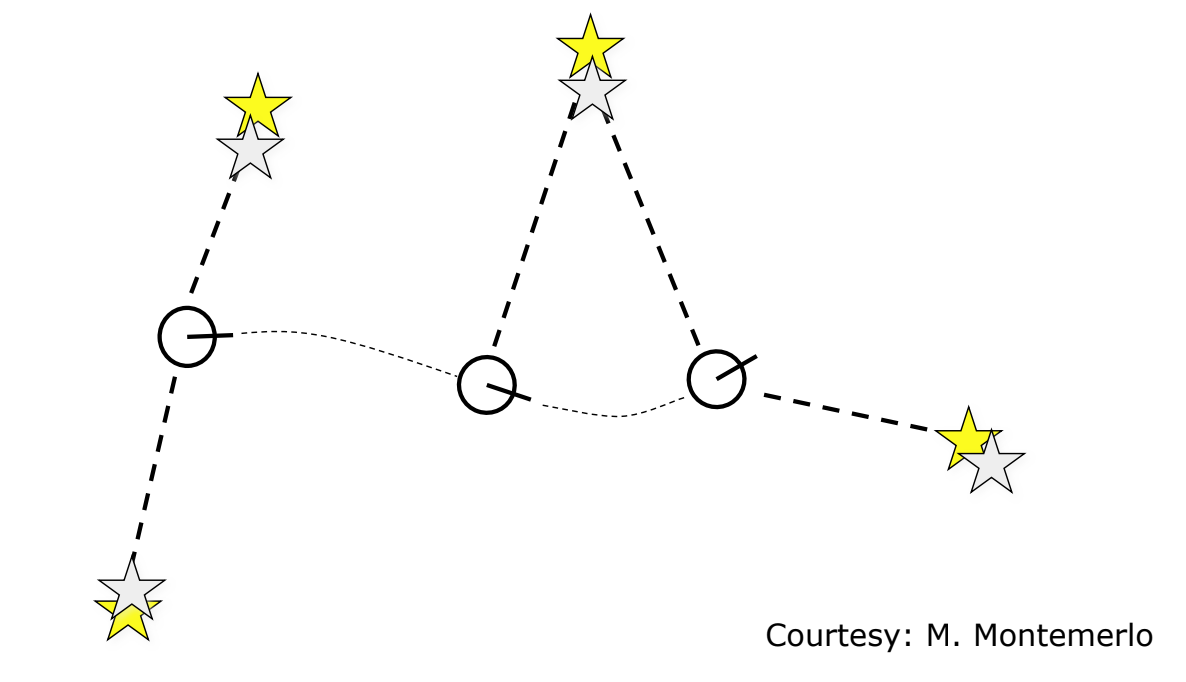
Mapping Example
랜드마크를 로봇의 위치를 통해 추정
흰색 동그라미 : 로봇의 위치
노란 별 : 실제 Landmark
회색 별 : 인지된 Landmark
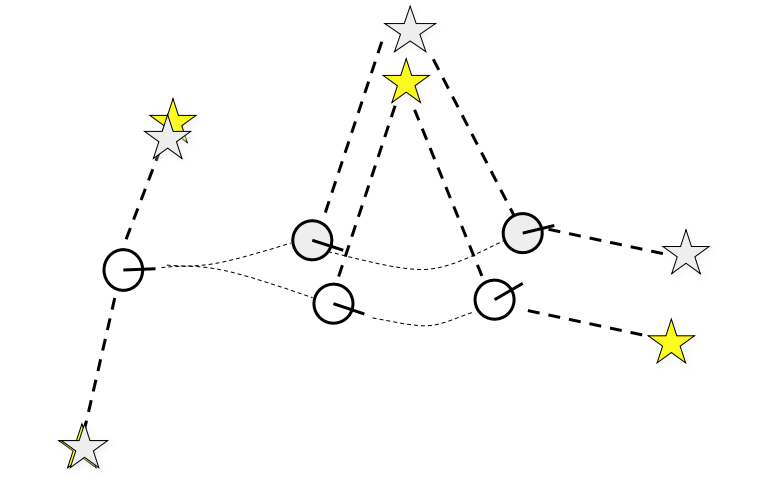
SLAM Example
로봇의 위치와 Landmark를 모두 추정
Loop Closure를 통해 Error 보정 가능
The SLAM Problem
- chicken-or-egg problem
→ a map is needed for localization
→ a pose estimate is needed for mapping
Definition of the SLAM Problem
- 주어진 데이터
- The robot’s control
- Observations
- The robot’s control
- 원하는 것
- Map of the environment
- Path of the robot
- Map of the environment
Probabilistic Apprsoaches
robot’s motion과 observations의 불확실성(uncertainty)를 표현하기 위해 확률 이론(probability theory)을 사용
따라서 SLAM Problem은 다음의 식으로 표현이 가능
는 probabilistic distribution을 의미
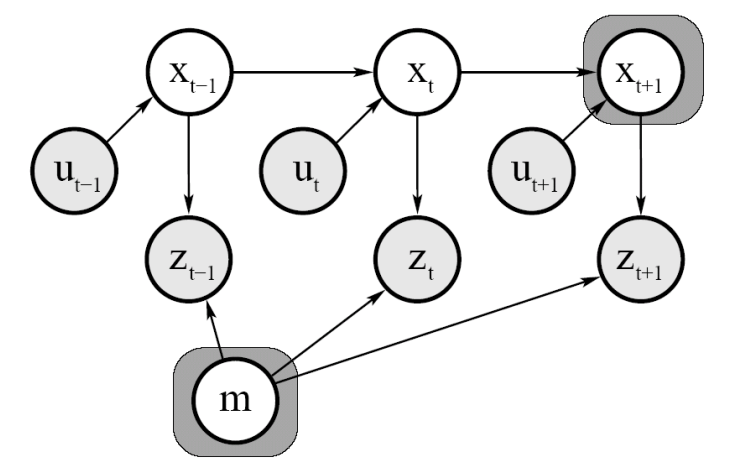
Graphical Model
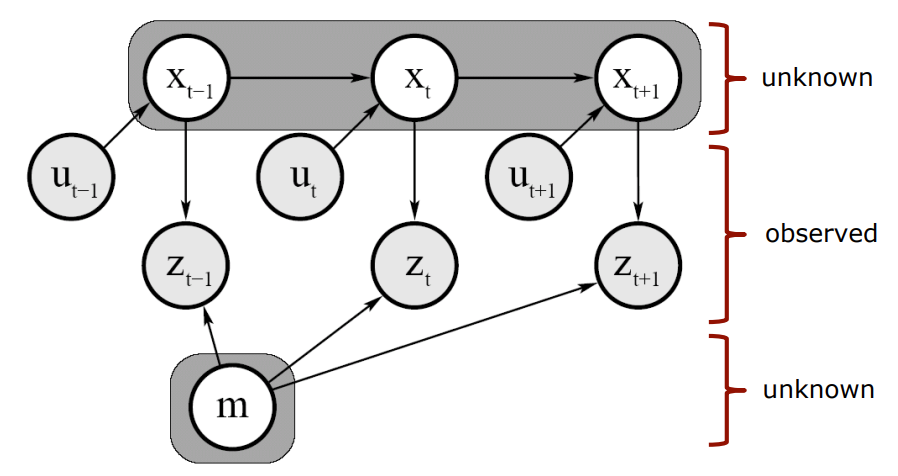 변수들간의 dependency를 표현함
변수들간의 dependency를 표현함
화살표는 어디서 어디로 impact를 주는지 의미
ex) 와 가 현재 위치 에 영향을 줌
Full SLAM vs. Online SLAM
- Full SLAM : estimate the entire path
- 위의 Graphical Model이 Full SLAM을 의미
- Online SLAM : seeks to recover only the most recent pose
Graphical Model of Online SLAM
 이전까지의 pose들로 marginalizing하는 것을 의미
이전까지의 pose들로 marginalizing하는 것을 의미
marginal probability : 모든 가능한 주변 확률의 경우의 수를 더해서 구하는 것을 의미
Full SLAM의 값을 모두 더해서 구할 수 있다.
Why is SLAM a Hard Problem
Robot path and map are both unknown
- 둘 중 하나가 정확하다면 다른 unkown data의 uncertainty가 줄어든다.
→ 반대로 말하면 둘 다 모르기 때문에 어려움을 의미
- 둘 중 하나가 정확하다면 다른 unkown data의 uncertainty가 줄어든다.
known vs. unknown correspondence
- 우리가 보는 랜드마크들을 모두 unique하게 구별하는 것이 불가능함
→ 판단을 잘못하면 문제가 생긴다.
- 우리가 보는 랜드마크들을 모두 unique하게 구별하는 것이 불가능함
∴ Data Association Problem
data association : 간단히 설명하자면 로봇이 어떠한 pose가 있을 때, 볼 수 있는 landmark들을 매칭시키는 작업
- Mapping between observations and the map is unknown
- 우리는 이것을 data association을 통해 uncertainty를 낮추려고 함
- Picking wrong data associations can have catastrophic consequences
- 만약 data association이 잘못됐을 경우 robot이 움직이 모든 path에 대한 판단이 잘못될 수 있음
Three Traditional Paradigms
- Kalman filter
- to estimate robot position and the landmark position
- Particle filter
- get rid of the Gaussian assumption about the world
- Graph-Based
- least squares formulation
- 요즘에 많이 사용됨
- 강의에서 이 방법을 다룰 것임
Motion and Observation Model
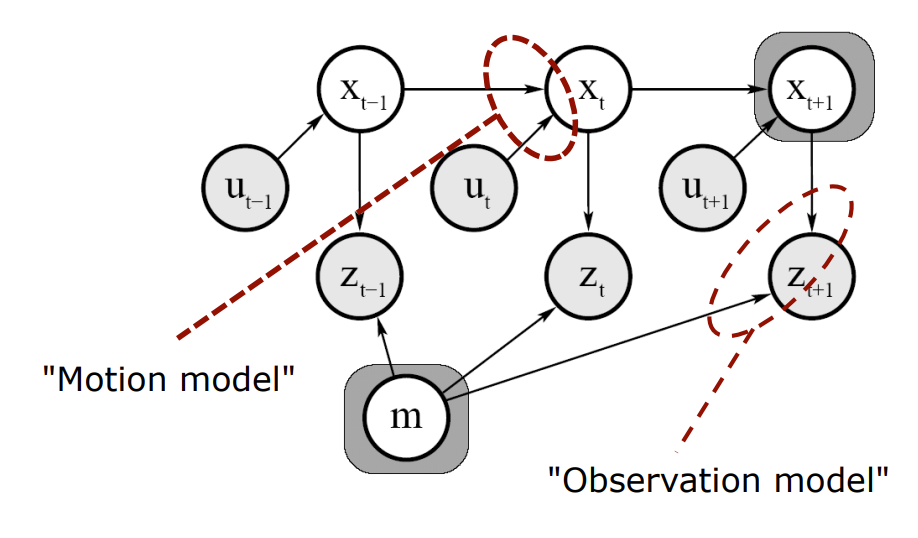
Motion Model
- describes the relative motion of the robot
- 이전 위치와 현재 움직임을 통해 현재 위치를 구한다.
Observation model
- relates measurements with the robot’s pose
- 현재위치(와 map)을 이용해 landmark의 위치를 구한다.